一次ceph rbd header watcher导致的iscsi故障处理
本博客所有文章采用的授权方式为 自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名 ,转载请务必注明出处,谢谢。
故障现象
2019-10-08T07:10:25.198Z cpu13:35761 opID=e02aea1b)Partition: 423: Failed read for "eui.6465336666353233": I/O error
2019-10-08T07:10:25.198Z cpu13:35761 opID=e02aea1b)Partition: 1003: Failed to read protective mbr on "eui.6465336666353233" : I/O error
2019-10-08T07:10:25.198Z cpu13:35761 opID=e02aea1b)WARNING: Partition: 1112: Partition table read from device eui.6465336666353233 failed: I/O error
2019-10-08T07:10:25.198Z cpu13:35761 opID=e02aea1b)Vol3: 785: Could not open device 'eui.6465336666353233:1' for volume open: No such partition on target
2019-10-08T07:10:25.198Z cpu13:35761 opID=e02aea1b)Vol3: 2790: Failed to get object 28 type 1 uuid 5a9d48e2-f2d01afa-cc00-000af797e698 FD 0 gen 0 :No such partition on
2019-10-08T07:10:25.198Z cpu13:35761 opID=e02aea1b)WARNING: Fil3: 2415: Failed to reserve volume f530 28 1 5a9d48e2 f2d01afa a00cc00 98e697f7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2019-10-08T07:10:25.198Z cpu13:35761 opID=e02aea1b)Vol3: 2790: Failed to get object 28 type 2 uuid 5a9d48e2-f2d01afa-cc00-000af797e698 FD 4 gen 1 :No such partition on
2019-10-08T07:10:48.777Z cpu17:44991579)NMP: nmp_ThrottleLogForDevice:2458: Cmd 0x84 (0x41330179b3c0, 0) to dev "eui.3939303832313261" on path "vmhba32:C0:T0:L12" Fail
2019-10-08T07:10:48.777Z cpu17:44991579)WARNING: NMP: nmp_DeviceRequestFastDeviceProbe:237: NMP
2019-10-08T07:11:05.203Z cpu14:44997166)Vol3: 731: Couldn't read volume header from eui.3939303832313261:1: Timeout
处理过程
iscsi的客户端和服务端都尝试过重启,现象还是一样。
检查esx 的该lun scsi 操作统计中可以看到失败的命令统计
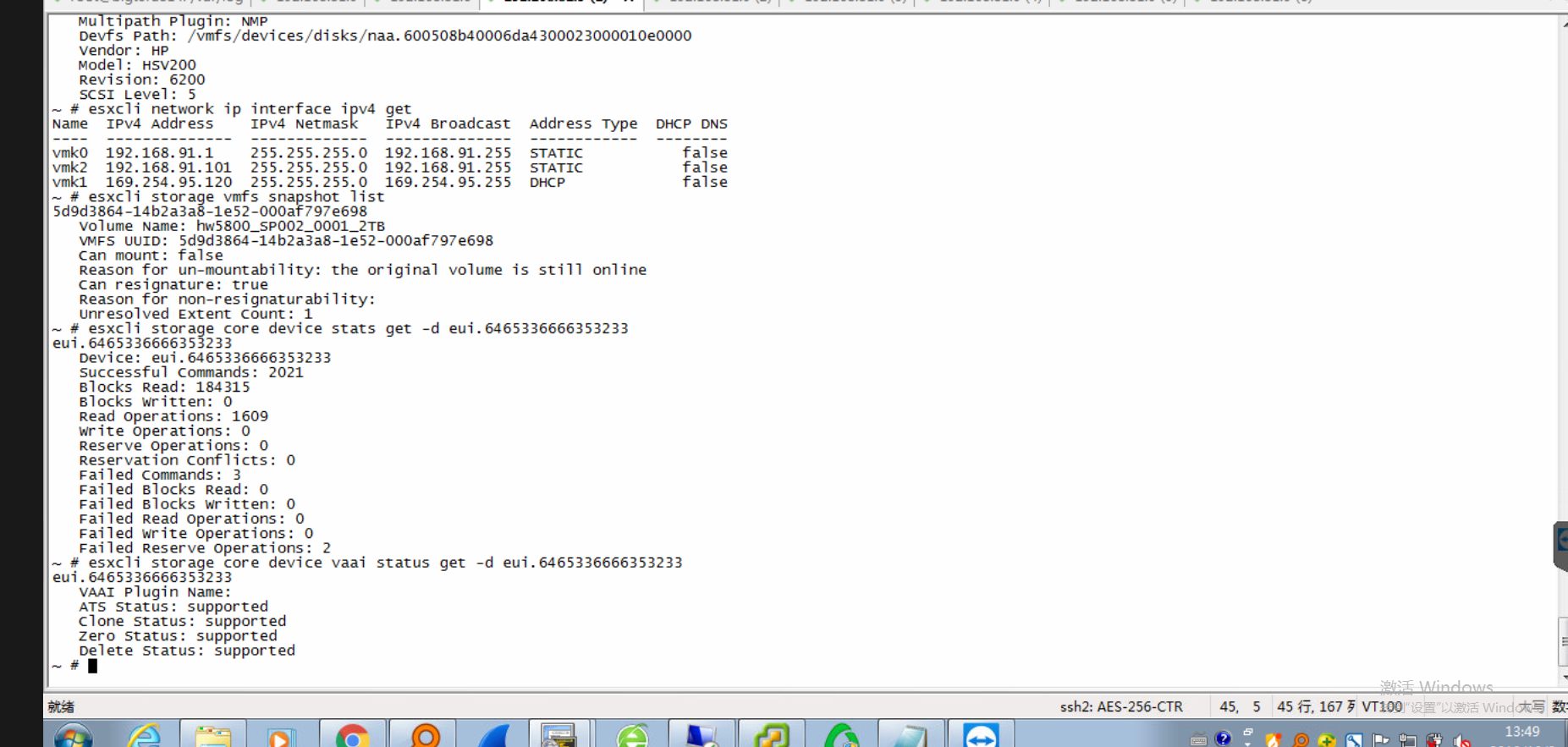
另外,esx 日志中看起来有超时的记录,联想到lun是在多台ESX主机之间共享的,lun的共享有专门的机制(reserve和release),SCSI-2和SCSI-3机制有些区别,详见后面的知识点记录。 所以怀疑是否是lun 的 lock出现问题了。
为了验证上面的怀疑,我们通过 一台linux系统挂载了该lun,手动 执行 SCSI的命令,模拟 lun的 reserve 动作,但是命令每次都是 40s的超时,然后失败返回。 基本和esx的日志吻合,lun已经无法正常响应reserve的命令。
所以,现在问题就定位在 为啥 lun无法响应 reserve 指令了。 lun的服务是由 内核模块 SCST提供,所以 现在需要知道 SCST 怎么了,只能打开内核 dynamic debug
内核的dynamic debug
首先通过 SCST的源码,找到关于 reserve和release相关的函数
SCST的源码,可以看到 reserve函数提供了 pr_debug(待确认这个pr_debug 是不是 内核专门预留给 debug 用的??)
532 static inline void scst_reserve_dev(struct scst_device *dev,
533 struct scst_session *sess)
534 {
535 EXTRACHECKS_BUG_ON(sess == NULL);
536 pr_debug("Old Holder: %p, New Holder: %p\n", dev->reserved_by, sess);
537 dev->reserved_by = sess;
538 }
通过 dynamic_debug打开的debug
该接口 提供了很多 可以debug的函数,可以 vim 找到需要的函数。
echo "func scst_clear_dev_reservation +lptf" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
echo "func scst_reserve_dev +lptf" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
通过sg相关的命令模拟 reserve指令(命令加 time 前缀,方便统计命令响应时间。)
sg_raw /dev/sdX 16 00 00 00 00 00 (Reserve)
sg_raw /dev/sdX 17 00 00 00 00 00 (Release)
命令效果(lab模拟)
root@wsg-70-3:~# time sg_raw /dev/sdd 16 00 00 00 00 00
>>> unknown pass through result category (1)
SCSI Status: Reservation Conflict
real 0m0.001s
user 0m0.003s
sys 0m0.001s
测试过程中发现,每次尝试去 reserve lun时,time统计的时间都是40s,正常情况下,reserve 指令应该很快就会返回。 看起来40s 应该是 软件上面的某个超时机制。考虑到底层为RBD,所以想到rbd的锁机制 和rbd header有关系。
于是,检查该rbd header的watcher,发现rbd header 竟然存在了2个 watcher (正常应该是一个watcher)。此时联想到该集群在 前几天,同事处理过osd leveldb膨胀问题,导致过集群长时间处于down+peering状态。
所以现在的问题转换为 如何删除这个 多出来的rbd header watcher
删除rbd header watcher
通过backlist的方式来删除,方法如下:
列出 rbd header watcher
rados -p rbd listwatchers rbd_header.7mjm6dk28jaj3
将有问题的 watcher 加入blacklist
ceph osd blacklist add 1.1.2.1:0/1193546917
检查 watcher 是否还存在,删除之后 再恢复 blacklist
ceph osd blacklist rm 1.1.2.1:0/119354691
检查blacklist 情况,确保已经恢复到初始状态
ceph osd blacklist ls
删除 watcher 之后,sg 模拟的 reserver命令立刻就返回了。
检查esx端,恢复正常。
总结
giant版本的rbd header watcher 在某些情况下(本次的情况是 集群出现过长时间的down+peering状态),可能不会自动释放,导致同一个rbd header 产生了多个 watcher,从而导致 scst层面的reserve 指令返回时间过长。 在 esx层面,表现为 对 iscsi lun 的设备加锁超时失败。
知识点记录
scst的debug 调整
cat /sys/kernel/scst_tgt/trace_level
恢复debug
echo "default" > /sys/kernel/scst_tgt/trace_level
iscsi lun的共享机制
通常来讲目前SCSI锁有两种类型:SCSI-2Reservation和SCSI-3 Reservation,这里SCSI-3Reservation也称之为Persistent Reservation。这两种类型的的锁是不能共存在一个Lun上的。
SCSI-2 Reservation只允许设备被发出加锁的Initiator访问,这里Initiator一般指HBA。比如HostA上的fcs0对访问的LUN加上SCSI-2锁,此时即使HostA上的fcs1也无法访问该Lun。所以SCSI-2 Reservation有时也被称为single-pathreservation。
SCSI-3 Reservation(PersistentReservation)是使用PR Key来对设备进行加锁。通常一台Host会有唯一的PR Key,不同的host,PRKey也不同。所以一般SCSI-3 Reservation通常被应用在多通路的共享环境下面。
内核的dynamic debug
准备后面会单独 写一篇 专门的文章,
scst的 reserv
echo "func scst_clear_dev_reservation =" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
echo "func scst_reserve_dev =" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
加选项
echo "func scst_clear_dev_reservation +lptf" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
echo "func scst_reserve_dev +lptf" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
kern.log
Oct 14 17:18:28 wsg-70-3 kernel: [356969.436003] [82419] scst_reserve_dev:536: Old Holder: (null), New Holder: ffff88011c870000
Oct 14 17:18:36 wsg-70-3 kernel: [356976.954242] [263065]: scst: scst_set_cmd_error_status:1698:Reservation conflict (dev tgt0_0, initiator iqn.1993-08.org.debian:01:6997c6813639, tgt_id 1)
Oct 14 17:18:36 wsg-70-3 kernel: [356976.954273] sd 3:0:0:0: reservation conflict
esx的 存储相关命令
查看所有 datastore
[root@localhost:~] esxcli storage filesystem list
Mount Point Volume Name UUID Mounted Type Size Free
------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ----------------------------------- ------- ------ -------------- --------------
/vmfs/volumes/2707af93-17b6f4d4 124-share 2707af93-17b6f4d4 true NFS 40008333393920 12798507614208
/vmfs/volumes/595d1290-79d25d9f-5c14-00e0ed438c52 datastore1 595d1290-79d25d9f-5c14-00e0ed438c52 true VMFS-5 231928233984 123346092032
/vmfs/volumes/5ce3ae6c-2f1dbf04-bb3b-00e0ed438c52 Presale-lun-v7-new 5ce3ae6c-2f1dbf04-bb3b-00e0ed438c52 true VMFS-5 6596801331200 5780643250176
/vmfs/volumes/5d06eb1f-f5cc5f8b-4ebc-00e0ed438c52 SEG-LUN 5d06eb1f-f5cc5f8b-4ebc-00e0ed438c52 true VMFS-5 21989964120064 4672265912320
/vmfs/volumes/5b8fa879-70bdee41-4848-00e0ed438c4e QA-lun-v7 5b8fa879-70bdee41-4848-00e0ed438c4e true VMFS-5 10994847842304 1681623351296
/vmfs/volumes/5a680f37-6036095e-cb6b-00e0ed438c52 5a680f37-6036095e-cb6b-00e0ed438c52 true vfat 4293591040 4255121408
/vmfs/volumes/7d3b9479-6b478943-643a-5a641dfcbd57 7d3b9479-6b478943-643a-5a641dfcbd57 true vfat 261853184 75464704
查看vmfs的 datastore
[root@localhost:~] esxcli storage vmfs extent list
Volume Name VMFS UUID Extent Number Device Name Partition
------------------ ----------------------------------- ------------- ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ---------
datastore1 595d1290-79d25d9f-5c14-00e0ed438c52 0 t10.ATA_____INTEL_SSDSC2BB240G4_____________________BTWL30940045240MGN__ 3
Presale-lun-v7-new 5ce3ae6c-2f1dbf04-bb3b-00e0ed438c52 0 eui.d8d980790ba184f2 1
SEG-LUN 5d06eb1f-f5cc5f8b-4ebc-00e0ed438c52 0 eui.99e91f03b82de449 1
QA-lun-v7 5b8fa879-70bdee41-4848-00e0ed438c4e 0 eui.ea3fcd1f5424a6f3 1
查看lun的统计
[root@localhost:~] esxcli storage core device stats get -d eui.99e91f03b82de449
eui.99e91f03b82de449
Device: eui.99e91f03b82de449
Successful Commands: 437865323
Blocks Read: 2390925674
Blocks Written: 25340206445
Read Operations: 31367192
Write Operations: 404557595
Reserve Operations: 0
Reservation Conflicts: 0
Failed Commands: 85
Failed Blocks Read: 512
Failed Blocks Written: 0
Failed Read Operations: 1
Failed Write Operations: 52
Failed Reserve Operations: 0
[root@localhost:~]
进程的暂停和 开始
SIGCONT 19,18,25 Cont Continue if stopped
SIGSTOP 17,19,23 Stop Stop process
Linux supports both POSIX reliable signals (hereinafter "standard
signals") and POSIX real-time signals.
Standard signals
First the signals described in the original POSIX.1-1990 standard.
Signal Value Action Comment
───────────────────────────────────
SIGHUP 1 Term Hangup detected on controlling terminal
or death of controlling process
SIGINT 2 Term Interrupt from keyboard
SIGQUIT 3 Core Quit from keyboard
SIGILL 4 Core Illegal Instruction
SIGABRT 6 Core Abort signal from abort(3)
SIGFPE 8 Core Floating point exception
SIGKILL 9 Term Kill signal
SIGSEGV 11 Core Invalid memory reference
SIGPIPE 13 Term Broken pipe: write to pipe with no
readers
SIGALRM 14 Term Timer signal from alarm(2)
SIGTERM 15 Term Termination signal
SIGUSR1 30,10,16 Term User-defined signal 1
SIGUSR2 31,12,17 Term User-defined signal 2
SIGCHLD 20,17,18 Ign Child stopped or terminated
SIGCONT 19,18,25 Cont Continue if stopped
SIGSTOP 17,19,23 Stop Stop process
SIGTSTP 18,20,24 Stop Stop typed at terminal
SIGTTIN 21,21,26 Stop Terminal input for background process
SIGTTOU 22,22,27 Stop Terminal output for background process
sg 工具包
root@node2:/usr/lib/cgi-bin/ezs3# dpkg -S /usr/bin/sginfo
sg3-utils: /usr/bin/sginfo
root@node2:/usr/lib/cgi-bin/ezs3# dpkg -l |grep sg3
ii sg3-utils 1.39-1 amd64 utilities for devices using the SCSI command set
root@node2:/usr/lib/cgi-bin/ezs3#
PR()
因為SCSI-2 RESERVE/RELEASE Command已經過時了,後來都是用SCSI-3開始定義的PR (Persistent Reserve)。
所以sg utils裡面也就沒有這兩個command的tool,要手動用sg_raw來打了
root@wsg-70-2:~# time sg_raw /dev/sdd 16 00 00 00 00 00
SCSI Status: Good
real 0m0.030s
user 0m0.005s
sys 0m0.002s
root@wsg-70-2:~# time sg_raw /dev/sdd 17 00 00 00 00 00
SCSI Status: Good
real 0m0.079s
user 0m0.000s
sys 0m0.002s
root@wsg-70-2:~#
lab 模拟lun的reserve 和release
sg_raw /dev/sdX 16 00 00 00 00 00 (Reserve)
sg_raw /dev/sdX 17 00 00 00 00 00 (Release)
2个 客户端 (node1和node2)同时 iscsi挂载上 同一个lun
reserve
node1 首先 对lun reserve
root@wsg-70-2:~# sg_raw /dev/sdd 16 00 00 00 00 00
SCSI Status: Good
root@wsg-70-2:~#
此时,node2 也尝试reserve,报错
root@wsg-70-3:~# sg_raw /dev/sdd 16 00 00 00 00 00
>>> unknown pass through result category (1)
SCSI Status: Reservation Conflict
root@wsg-70-3:~#
如果此时 node1 上,将 上面的reserve 释放掉
root@wsg-70-2:~# sg_raw /dev/sdd 17 00 00 00 00 00
SCSI Status: Good
root@wsg-70-2:~#
此时 ,node2 再次尝试 reserve,就可以顺利完成了
root@wsg-70-3:~# sg_raw /dev/sdd 16 00 00 00 00 00
SCSI Status: Good
root@wsg-70-3:~#
scsi命令读数据
root@wsg-70-2:~# sg_raw -r 1k /dev/sdd 12 00 00 00 60 00
SCSI Status: Good
Received 66 bytes of data:
00 00 00 06 02 3d 08 10 02 42 69 67 74 65 72 61 20 ....=...Bigtera
10 56 69 72 74 75 61 6c 53 74 6f 72 5f 53 63 61 6c VirtualStor_Scal
20 30 37 30 30 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0700............
30 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 8b 09 60 04 63 .............`.c
40 04 c0 ..
root@wsg-70-2:~#
sdc是vm中 虚拟磁盘
root@wsg-70-2:~# sg_raw -r 1k /dev/sdc 12 00 00 00 60 00
SCSI Status: Good
Received 36 bytes of data:
00 00 00 02 02 1f 00 00 73 56 4d 77 61 72 65 20 20 .......sVMware
10 56 69 72 74 75 61 6c 20 64 69 73 6b 20 20 20 20 Virtual disk
20 31 2e 30 20 1.0
root@wsg-70-2:~#